Transformer Models in NLP
Understanding how attention works in transformers
- Highlights of Transformers
- Component of Transformer
- Applications of Attention
- Embeddings and Softmax
- Positional Encodings
- Why use Self Attention?
- Transformers in a Nutshell
- Dropout
- Label smoothing
Earlier Seq2Seq used to make use of encoder,decoder architecture. The best models make use of attention mechanisms. Attention mechanisms have also become an integral part allowing modelling of dependencies without regard to their respective distances. In this article, we look at another architecture as introduced in Attention is all you need.
Highlights of Transformers
- Transformers outperform both recurrent and convolutional models
- Well suited for language understanding
- Superior than Seq2Seq
- Requires less computation,transformers are faster to train
- RNNs/CNNs can’t make proper use of parallel processing hardware (GPU/TPU),
- Can work in parallel (difficult to learn dependencies from distant positions) . Takes constant number of operations. Works by averaging attention weighted vectors (dealt in multi head attention step)
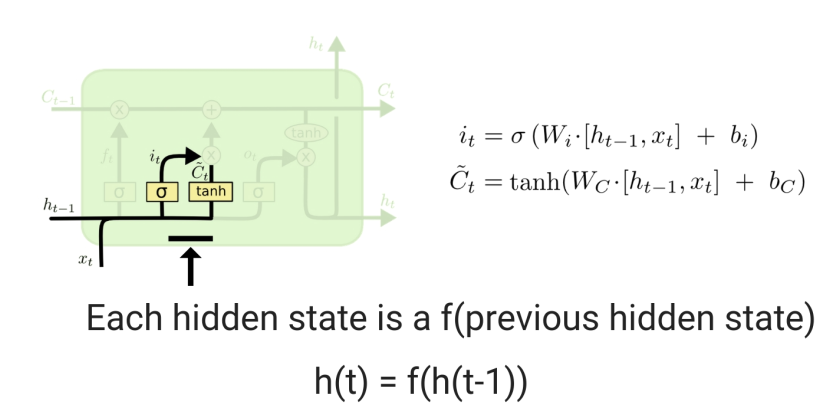
Recurrent models generate hidden states H(t) as a function of previous hidden state H(t-1), this precludes parallelization within training examples which becomes crucial when lengths of sequences becomes large.
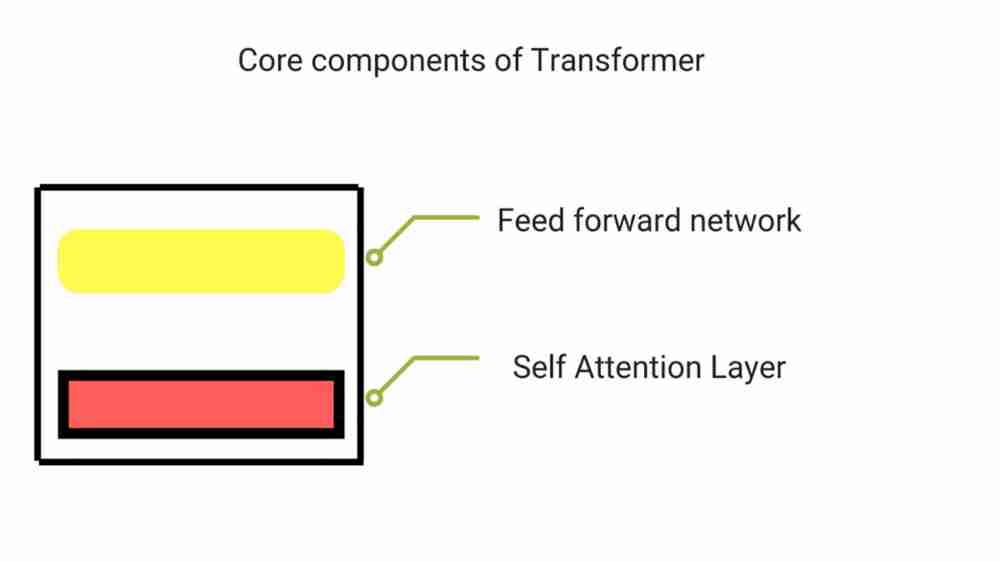
Transformer consist of self attention layer and a feed forward network. Self attention models relationships between all words irrespective of their positions in a sentence.
In transduction models, encoder maps an input sequence of symbol representations to a sequence of continuous representations. The decoder then generates an output sequence of symbols one element at a time. They are auto regressive which means consuming previously generated symbols as additional input when generating the next.
Component of Transformer
Encoder
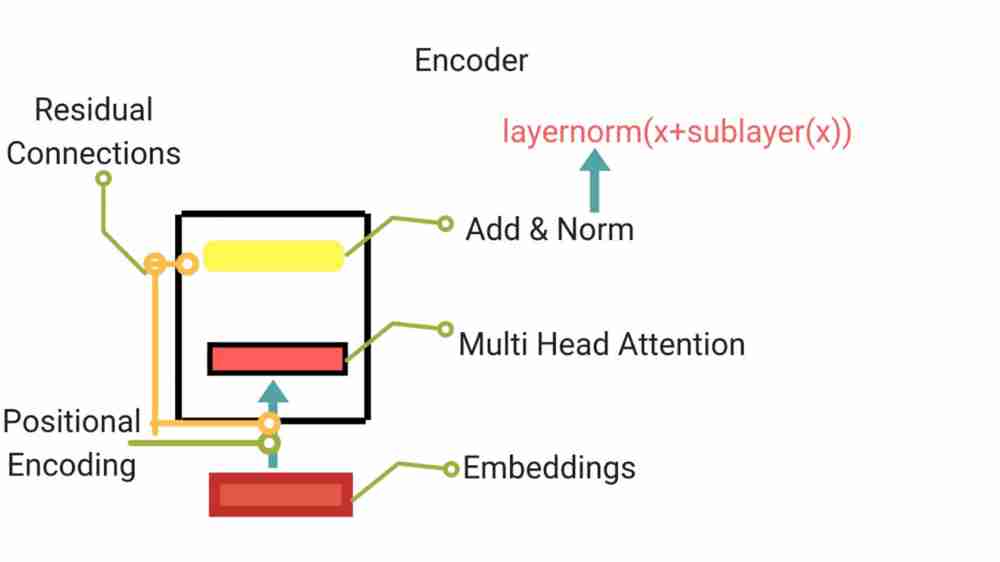
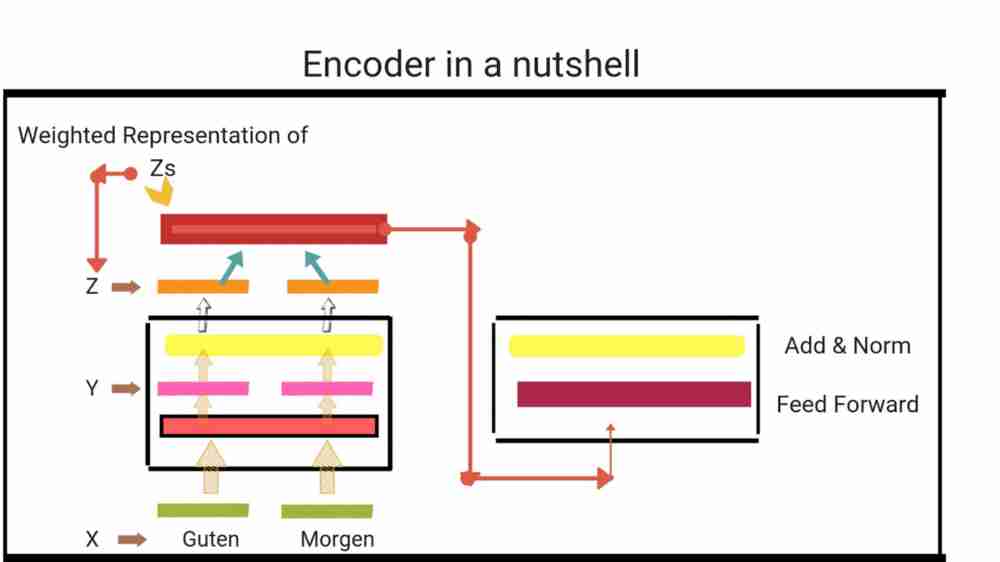
Each layer has two layers . First is multi head attention layer mechanism and the second one is simple position wise feedforward network. They also make use of residual connection around each of sub layers.
Skip connection works as follows:
LayerNorm(x+sublayer(x))
Sublayer(x) is the function that is being generated from the sublayer. To make use of residual connection when performing addition, all sub layers as well as embedding layers produce output of specified dimension.
Encoder looks at all the words and creates a new representation of those words after processing word through it’s components. Each word has flows through it’s own path (that means getting processed in parallel), self attention has shared dependencies of these words but feed forward network doesn’t have it.
Self attention layer is a process of relating different parts of sequence in order to compute representation of sequence) computes every word in sentence attention scores of all the words with respect to the current word. This score denotes how much value a particular word needs to given as compared to present word.
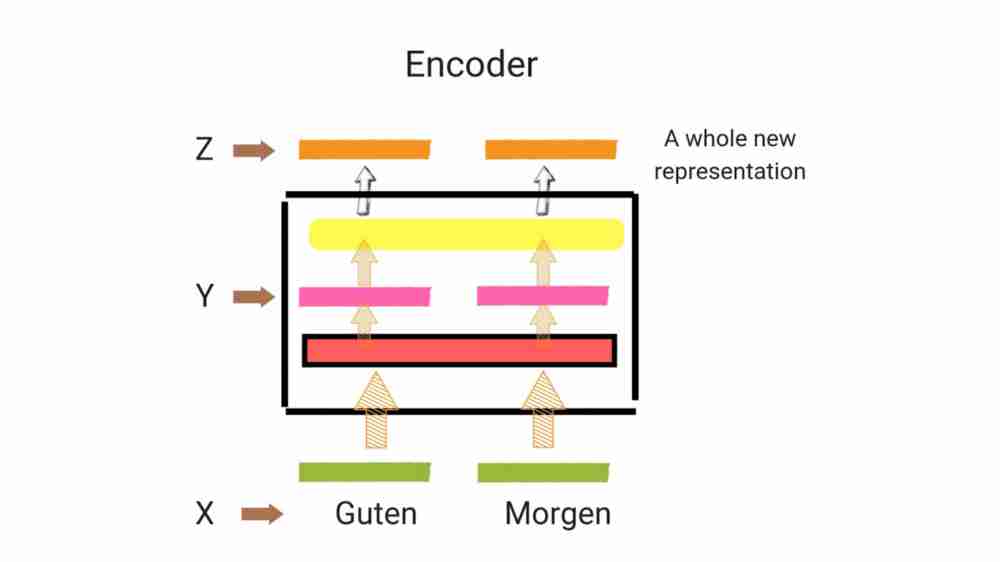
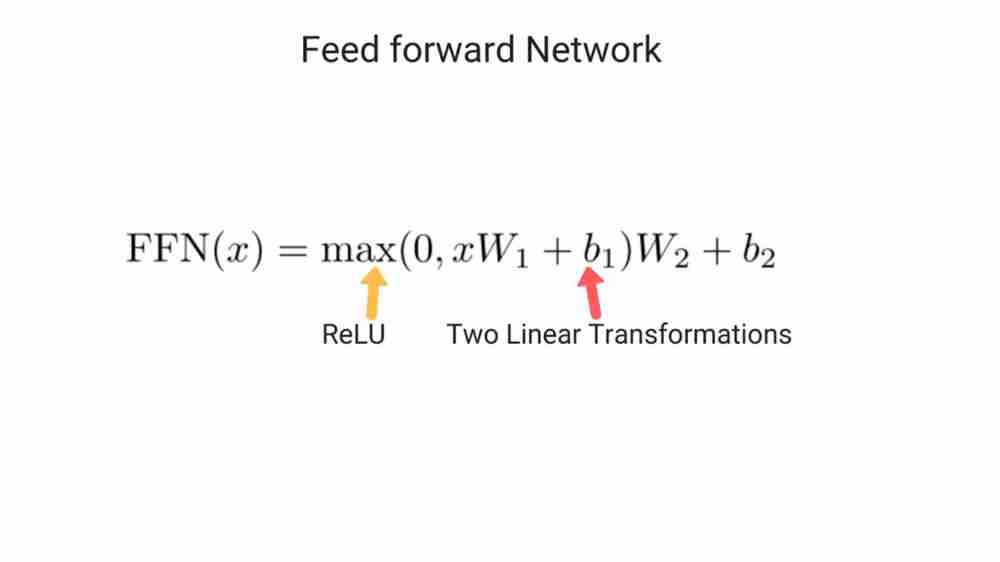
Feed forward network expects a matrix as input. These attention scores are used as weights for a weighted representation of all words and then fed to feed forward network.
In NMT,encoder creates representation of words,decoder then generates word in consultation with representation from encoder output. Transformer starts with embeddings of words,then self attention aggregates information from all the words and generates new representation per word from the entire context
Decoder
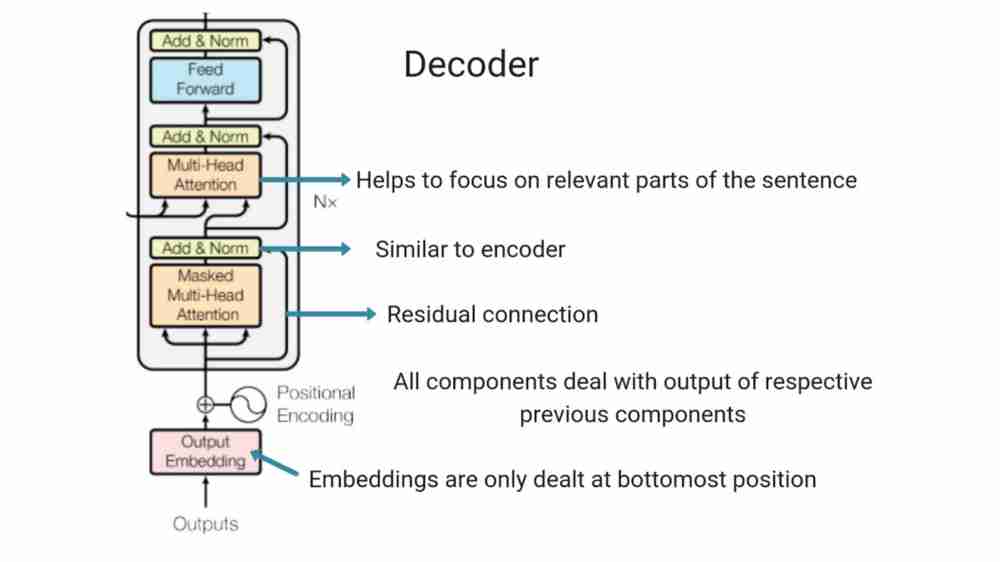
It is also composed of same number of identical layers. It also comprises of two sub layers present in each layer of encoder, in addition it also has one layer which performs multi head attention over the output of encoder stack. It also makes use of residual connection with layer norm. To prevent positions from attending to subsequent positions, self attention layer has also been modified.
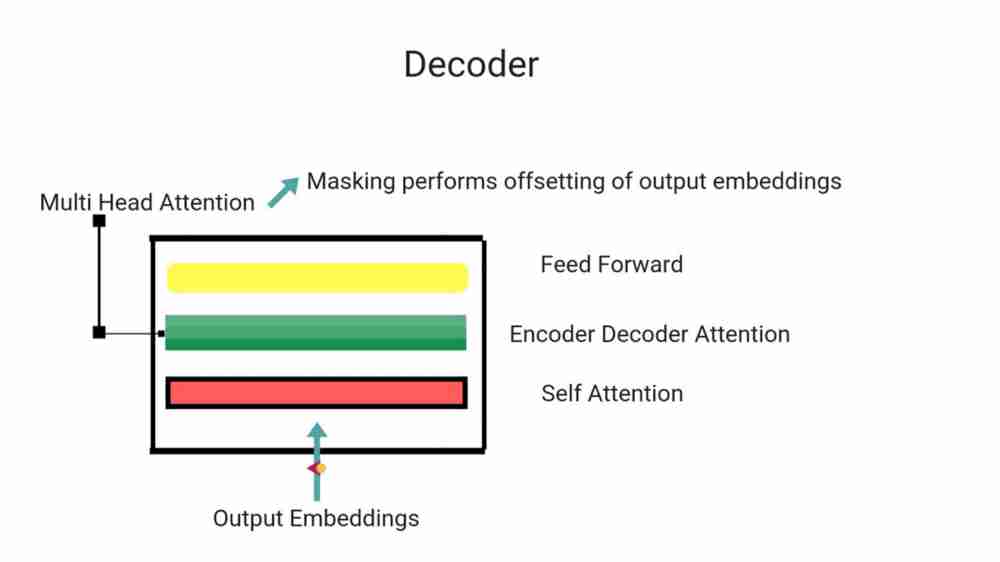
Such masking makes sure that output embeddings are offset by one position. It ensures that prediction of position i can depend only on known outputs at positions less than i
It attends to previously generated word+final representations generated from encoder. We can also visualize how much attention transformer pays to other parts of sentence when processing the current word ,thus giving insights to how information flows. Encoder decoder attention in decoder helps it to focus on relevant parts of the the parts of sentence.
The embedding representation is dealt in the bottom most encoder and the rest of the encoders deal with outputs of other encoders. Encoders receive a list of vectors (default size=512)
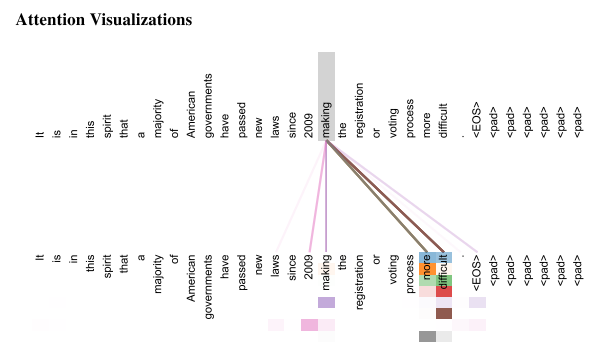
Attention
Can be described as a mapping a query and set(key value pairs) to an output. Query,Keys, Values are all vectors.
Output can be computed as weighted sum of values where weight assigned to each value is computed by compatibility function of query with corresponding key . There are two types of ways attention is usually computed:
Scaled Dot product Attention
-
Queries, Keys and Values are computed which are of dimension dk and dv respectively
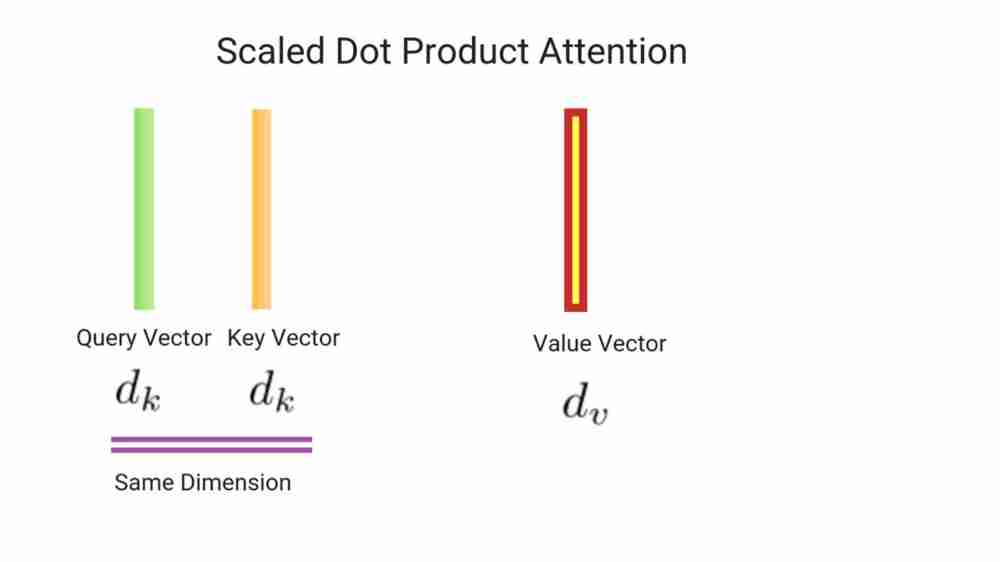
- Take Dot Product of Query with all Keys and divide by scaling factor sqrt(dk)
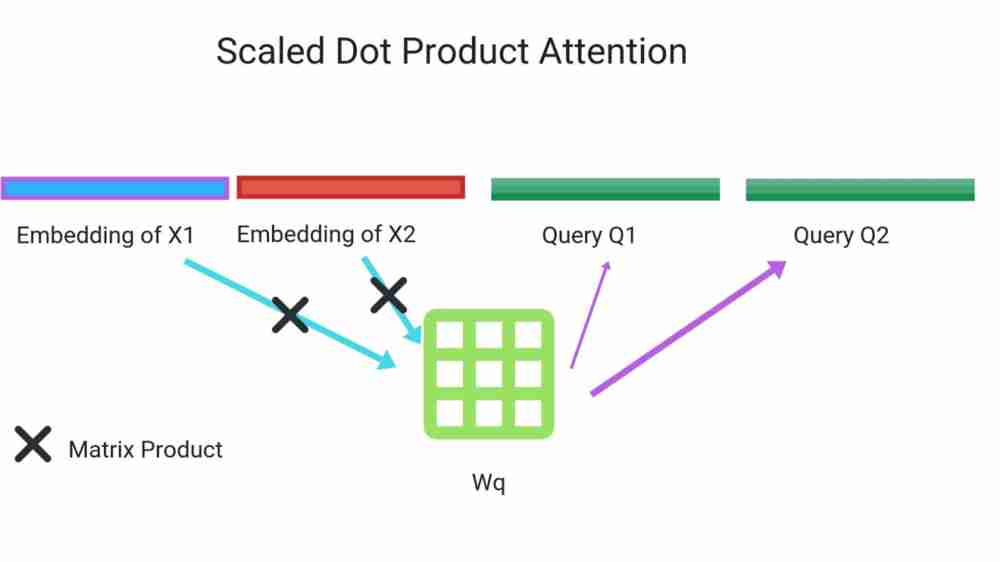
- We compute attention function on set of queries simultaneously packed together into matrix Q
- Keys and Values are packed together as matrix
- Most common attention functions are additive and dot product
This is similar to dot product attention (only difference being scaling factor).
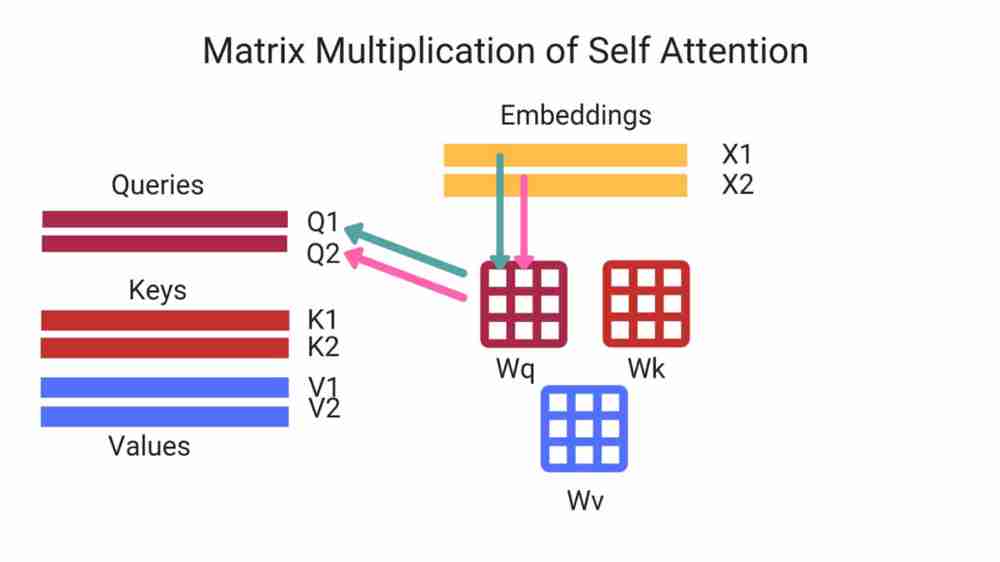
Matrix multiplication of self attention
We perform calculation of Q,K,V vectors and then pack all our embeddings into a matrix and multiply the weight matrices we’ve obtained from training.
Additive Attention: Computes compatibility function using feed forward network with single hidden layer
-
These two methods are similar in theoretical complexity although dot product attention is much faster and space efficient in practice. It can be optimized with matrix multiplication
- If dk is small, these two methods of computing attention function may perform similarly. If dk is large additive may outperform dot product method of computing attention
- Dot product grows in magnitude with large values of dk, it may push softmax into regions where it may have small gradients and then it can have a hard time coming out of saddle points. To deal with this, we use this scaling factor of sqrt(dk)
MultiHead Attention
We linearly project Q,K,V vectors h times with differently learned projections of following dimensions: dq,dk,dv. Perform attention function in parallel which outputs vector of dimension dv. These are then concatenated and then projected again
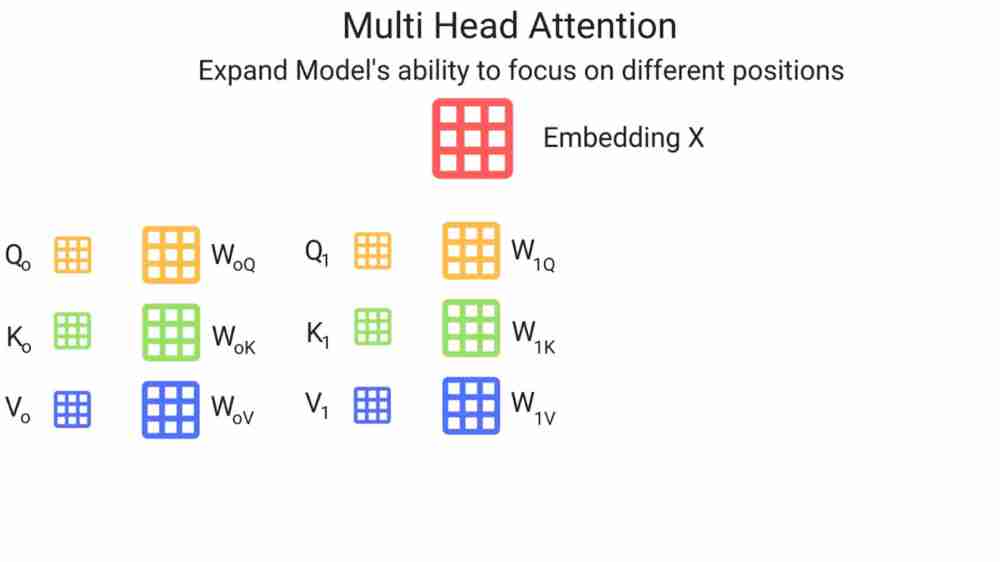
We linearly project Q,K,V vectors h times with differently learned projections of following dimensions: dq,dk,dv. Perform attention function in parallel which outputs vector of dimension dv. These are then concatenated and then projected again
Allows model to jointly attend to different representations subspaces at different positions. We’ve multiple set of Q,K,V matrices (if transformer uses n heads, we will have n matrices) . Each of these are randomly initialized and then after performing training, each set is used to project input embeddings into different representation subspace.
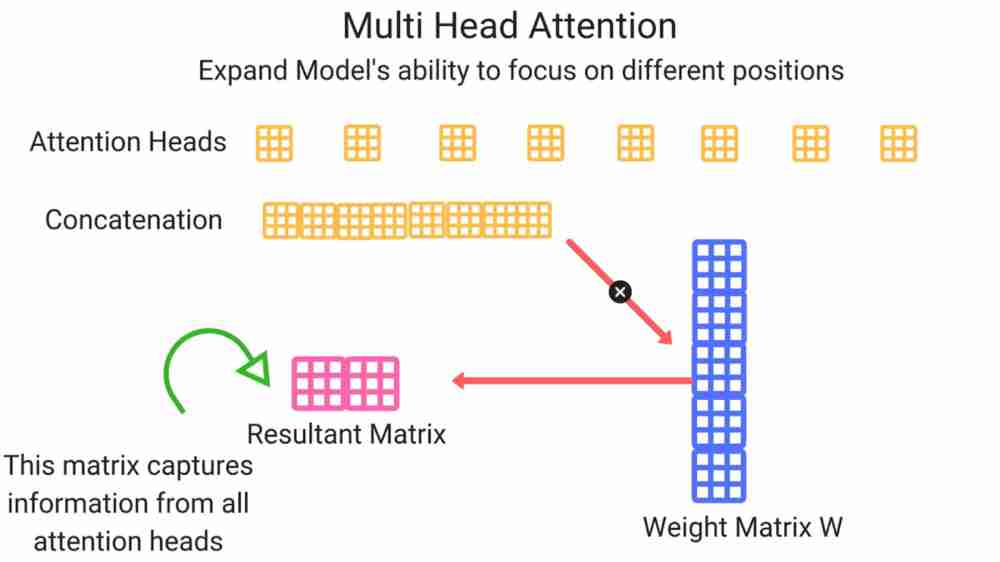
For input to feedforward network, we take all these matrices and concatenate them by multiplying them with an additional matrix since the feedforward network requires only one input tensor.
Applications of Attention
We obtain Query vector from previous decoder layer and Key,Value vectors are obtained from output of Encoder. This mimics Seq2Seq models.
- Self attention in Encoder: In self attention, K,V,Q vectors come from same place, Each position in encoder can attend to all positions in previous layer of encoder
- Self Attention in Decoder allows position in decoder to attend to all the positions in the decoder and up to current position . Leftward information flow is prevented to preserve autoregressive property
Embeddings and Softmax
Just like other Sequence transduction models, we are using learned embeddings to convert input,output tokens into a vector. These happens at the base of encoder. In the first bottom encoder, we would be feeding these word embeddings and for the rest, we would be feeding output of encoders. We then make use of linear transformation and softmax function to convert the decoder output to predict probabilities for each possible token we have to consider. Same matrix is being shared for these two embedding layers and pre-softmax linear transformation
Positional Encodings
This model doesn’t make use of either convolution or recurrence, to make sure that model is making use of order of sequence, we’re required to place this information in the form of vector to each of input embeddings at the bottom of encoder and decoder stacks. This vectors helps model to learn a specific pattern of determining relative position of words in sequences. This is being called positional encodings. Intuitively, adding these values to embeddings provide meaningful distance between vectors themselves after they get projected as Q,K,V and in dot product attention.
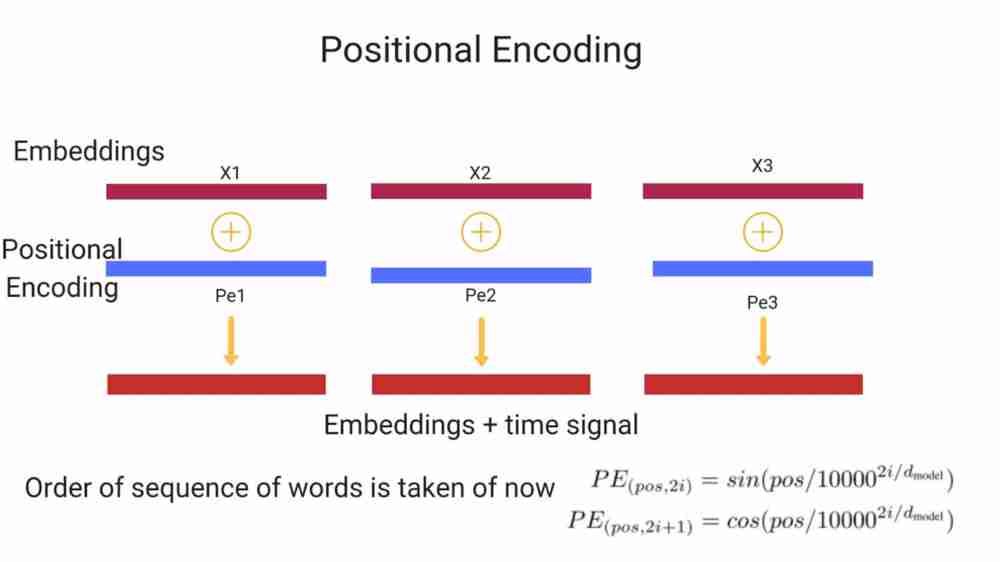
Sinusoidal function is being considered as it may allow model to interpolate better for longer sequences. Learned positional embeddings were also made use of, but they performed practically same.
Why use Self Attention?
Comparing convolutional and recurrent operations which are commonly used for mapping variable length sequences of symbol representations to the output (eg. hidden layer in seq2seq).
Transformers have an edge over:
- Complexity per layer
- Amount of computation that can be parallelized
- Path length dependencies. (higher it is, more difficult it is for RNNs).
Self Attention connects all positions with constant number of sequentially executed operations. In terms of computational complexity, self attention is faster than recurrent operations when (seq length < representation dimensionality d)
In case of convolutions:
- Kernels do not connect all pairs of input and output
- Requires stack of conv layers in case of contiguous kernels
- More expensive operations than recurrent
Transformers in a Nutshell
Each sublayer makes use of residual connections which is them followed by layer normalization. We take embedding, create vectors along with positional encodings, feed them to self attention. Then it gets processed by layer norm layer (adds and normalizes two matrices). Then the output vector is placed towards feedforward network which then outputs it towards layer norm. The generated vectors from output of top encoders are transformed into set of K,V vectors which are then passed on to decoder as well. The intuition behind them is that encoder decoder attention in decoder layer helps decoder to focus on appropriate places in input sequence.
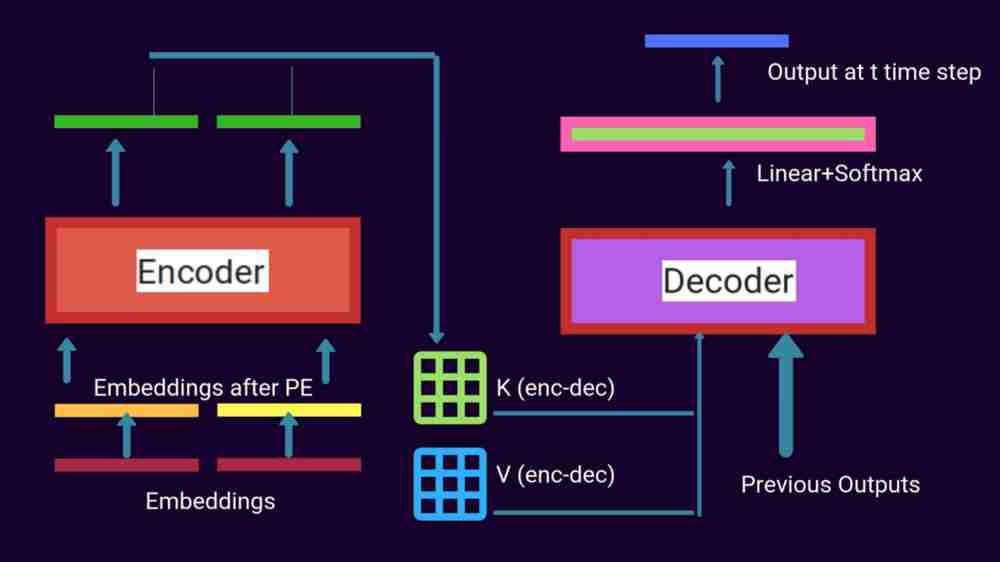
In the case of decoder, self attention layers are only allowed to attend to earlier positions in the output sequence . We mask future positions before softmax. The linear layer at the end of decoder is responsible for converting the resultant vector into a very large logit vector. Softmax turns all the scores into probabilities . We take the one with the highest probability and the word associated with it is chosen.
Dropout
Residual dropout was used for carrying out this experiment. It’s being used in two places
- Output of each sub layer before it is added to input layer and normalization.
- It has also has been applied to the sums of embeddings and positional encodings in both encoder decoder stacks
Label smoothing
It can also be used. It hurts perplexity,as the model learns to be sure but improves BLEU score and accuracy
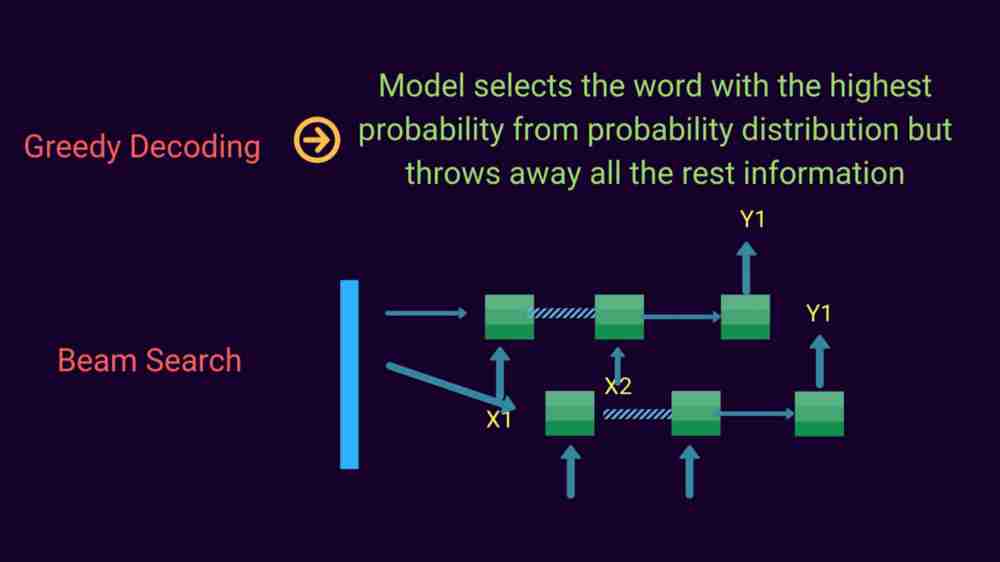
In this work, model selects the word with the highest probability from probability distribution but throws away all the rest information. This is greedy decoding. Another way of carrying out this process, is to use beam search. In that, we have a beam size. As per beam size, we consider those n words (beam size being equal n) and consider those n words, then in the next run, we consider the n+1 word considering the output positions in previous n word whichever produced the least error.